What is provisioning?
Provisioning is the process of setting up and delivering resources, services, or functionality to individuals or systems. It involves gathering and implementing the infrastructure or parts required for a specific task or function.
Provisioning occurs in various settings, including network administration, telecommunications, and cloud computing. It’s a frequently used term in the information technology (IT) industry that describes the distribution and configuration of computing resources such as servers, storage, networking hardware, software, and applications.
It requires companies to establish software configurations, user accounts, and access privileges and then deploy and configure these resources to fulfill particular needs. The build can be manual or automated with the help of user provisioning software.
Types of provisioning
Provisioning is key in managing governance across IT resources. Organizations can make use of several types.
- Server provisioning involves installing and configuring software, setting up physical or virtual hardware, and connecting it to storage, network, and middleware components.
- Cloud provisioning creates a fundamental infrastructure for a company’s cloud environment. Once the network elements and services are installed and cloud infrastructure is set up, provisioning helps make resources and services available within the cloud.
- User provisioning concentrates on identity management. It grants users access to corporate services and applications based on their permissions and needs.
- Network provisioning assists users with configured devices like routers, switches, and firewalls. It also allocates IP addresses, conducts health checks, and gathers information necessary for the users. In telecom, network provisioning refers to providing telecommunication services.
- Service provisioning involves configuring IT-dependent services to end users and maintaining relevant data. For example, the system gives the new employee access to the software as a service platform, login access, and other system privileges according to their role.
Benefits of provisioning
Organizations must ensure the correct employees have access to suitable applications and infrastructure to reap benefits and avoid security threats. Given below are some of the advantages of using provisioning.
- Better security. Effective provisioning safeguards user privileges and protects sensitive information from data threats. Administrators can set user permissions without direct access to any of their private information, which makes the company’s overall security posture look better. Even if an employee wants to change their passwords, provisioning makes it easier and simpler to provide support.
- Regulation enforcement. Good IT provisioning improves security by working to enforce regulatory compliance across the organization. It ensures that essential standards are understood and followed.
- Higher productivity. As provisioning deals with managing user credentials and identities, it reduces time-consuming and ineffective procedures for handling individual application passwords and other difficulties. This means better employee productivity.
- User-centric administration. Provisioning lets administrators centralize the management of user application accounts. Provisioning various accounts across the company’s infrastructure and automatically updating application credential changes makes admins’ work easier.
- Enhanced return on investment (ROI). User account management used to take a lot of time and financial commitment. Provisioning helps companies reduce these expenses, swiftly recovering their investment and transforming account management into a crucial asset.
Best practices for provisioning
Automated provisioning is an effective method for managing user lifecycle and identities. Following some essential best practices will maintain a robust security posture.
- Automate. Automating wherever possible means lowering the risk of inaccuracies and security threats or issues. This helps the onboarding and offboarding processes. Automated provisioning and deprovisioning allow a secure and seamless transfer whenever an employee is hired, leaves an organization or is assigned a new tool.
- Deprovision. Remove any access as soon as an employee leaves the organization. Unauthorized access can result in data loss or other security breaches.
- Layer security. Give more power to IT and human resources administrators with control over roles, access, and security policies. Setting additional policies means these administrators can improve and secure applications and permissions for better system access protection.
- Monitor. Systems remain secure as long as the system users don’t take undue advantage of it. Provisioning lets system administrators analyze the status of employees and their access. Following up ensures no individual has more privileges than required and no accounts exist for deactivated users.
- Adopt single sign-on (SSO). User provisioning systems can be connected with SSO from the same vendor. It saves a lot of human time and errors and fosters security.
Provisioning vs. deprovisioning
Some may confuse provisioning and deprovisioning, but the two have key differences.
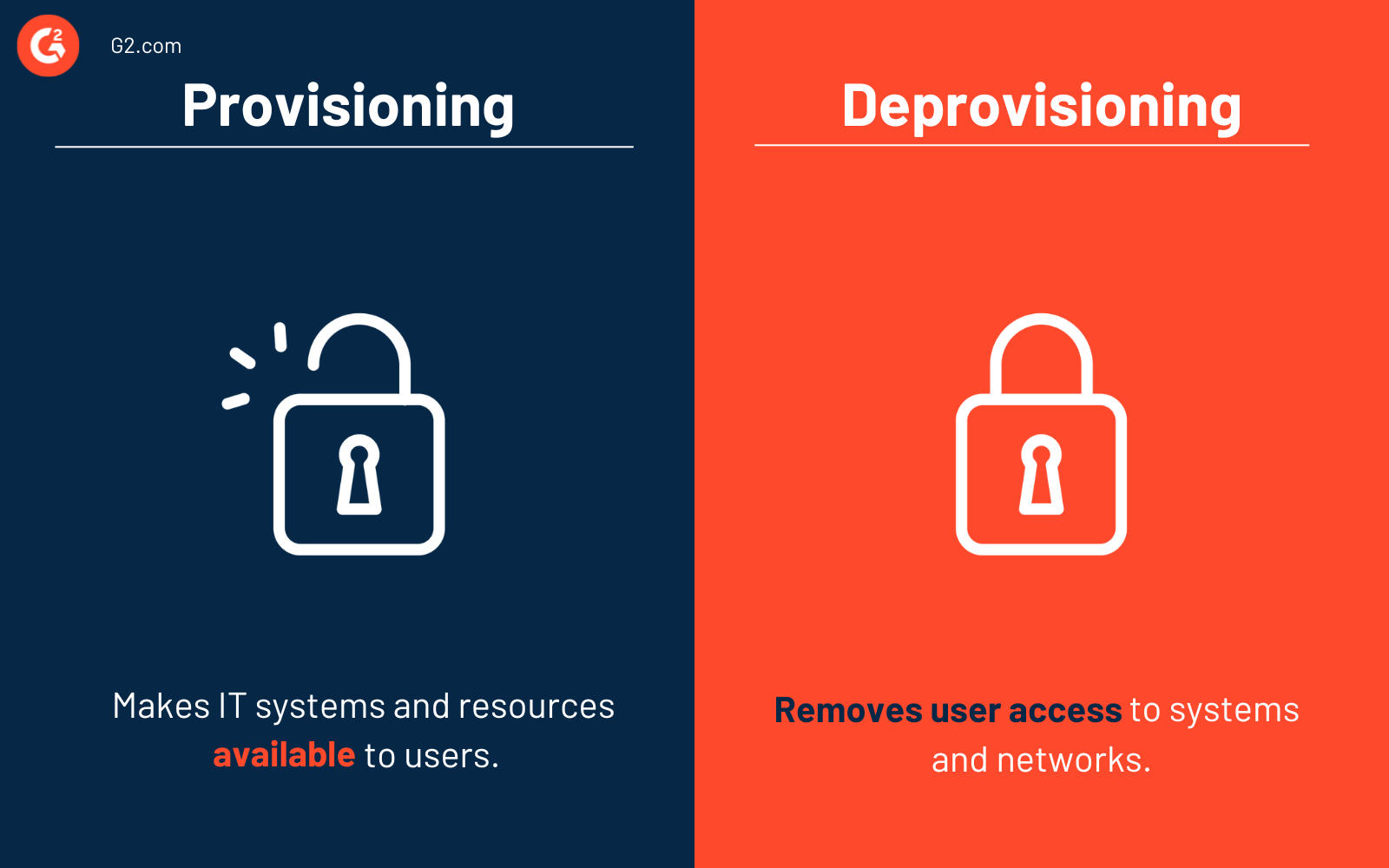
Provisioning makes IT systems and resources available to users. Deprovisioning, on the other hand, removes user access to systems and networks. Both provisioning and deprovisioning are vital steps in securing IT systems and applications.
Any organization that plans to advance its security posture should plan effective automated user provisioning and deprovisioning. They’re both an important part of the employee lifecycle.
Learn more about identity and access management (IAM) to take care of access permissions and prove compliance at scale.

Sagar Joshi
Sagar Joshi is a former content marketing specialist at G2 in India. He is an engineer with a keen interest in data analytics and cybersecurity. He writes about topics related to them. You can find him reading books, learning a new language, or playing pool in his free time.