What is continuous integration?
Continuous integration (CI) is a DevOps software technique developers use to routinely merge their code changes into a central repository, followed by the execution of automated builds and tests. In a word, CI is the build or integration stage of the software release process.
CI includes both an automation component and a cultural component. Continuous integration's main objectives are to find and fix bugs more quickly, enhance software quality, and shorten the time it takes to validate and publish new software updates. Many organizations use continuous integration tools to build, package, and test their software continuously.
Previously, developers on a team might spend a lot of time working alone and only merge their modifications to the master branch once completed. This resulted in bugs building up for a long time without being fixed, making merging code changes challenging and drawn/out. These issues make it more challenging to provide customers with updates quickly.
How does continuous integration work?
Continuous integration is typically implemented using tools and technologies like version control systems. By automating the build and testing process, CI guarantees that code changes are thoroughly tested and integrated smoothly into the main codebase, improving the quality and speed of software development.
Below is a step-by-step overview of the CI process.
- Code changes. Developers make changes and submit the code to the repository.
- Monitor repository. The CI system monitors the repository for changes. When a change is detected, it triggers the build process.
- Compiling code. The build process involves compiling the code and running automated tests to verify that the changes do not break the existing code.
- Integration into the codebase. The changes are integrated into the main codebase if the build and tests are successful.
- Fix bugs. If the build or tests fail, the developers are notified so they can identify and fix the issues.
- Deploy code. Once the changes are integrated, the system deploys the updated code to a staging or production environment.
- Continuous monitoring. The CI system continues to monitor the codebase for new changes and repeats the process as new changes are made.
Benefits of continuous integration
Organizations are eager to adopt continuous integration for their development projects. Enhancing the effectiveness and caliber of software development processes is just one way CI supports the companies that use it. Below are more of the advantages continuous integration provides to its users.
- Early detection of bugs. CI detects bugs early in the development cycle before they become more difficult and costly to fix. Developers can quickly locate and repair issues by integrating code changes frequently.
- Faster time-to-market. Developers have an easier time delivering new features and updates when they use CI. The less time a company takes to bring new software to market, the faster it can gain a competitive edge.
- Improved collaboration. Developers can collaborate better by ensuring everyone is working on the same code version and providing a shared repository where changes can be tracked and reviewed. The risk of conflicts decreases while the overall quality of the codes improves.
- Greater confidence in code integrity. Test and verify code changes with CI, giving developers greater confidence in the quality of the code. The result is error-free code with greater software stability.
- Easier maintenance. CI simplifies maintaining and updating software over time by providing a reliable and automated process for integrating code changes. This reduces the cost and effort required for ongoing maintenance and support.
Features of continuous integration
Several features of CI enable developers to automate the build and testing process and ensure that code changes are integrated smoothly into the main codebase. Some of these features include:
- Automated build. Refine the build process so that changes to the codebase can be built automatically and without human intervention. This helps to ensure that the code is always in a buildable state.
- Automated testing. Automate testing to ensure that code changes are thoroughly vetted before they’re integrated into the main codebase. This identifies and addresses any issues early in the development cycle.
- Continuous integration server. Build and test code changes as they’re submitted to the shared repository with the CI server so the codebase is always up-to-date and error free.
- Code repository. CI relies on a code repository, the central location for storing and managing code changes. It makes certain all developers are working on the same code version and that changes can be tracked and reviewed.
- Notification system. In order to guarantee that issues are handled as soon as possible, alert developers to the status of the build and testing process through the notification system.
- Continuous feedback. Pinpoint and resolve any obstacles that arise through continuous feedback. The feedback will reduce the risk of delays and errors.
Continuous integration vs. continuous delivery
It's common to confuse continuous integration with continuous delivery, but the two are very different.
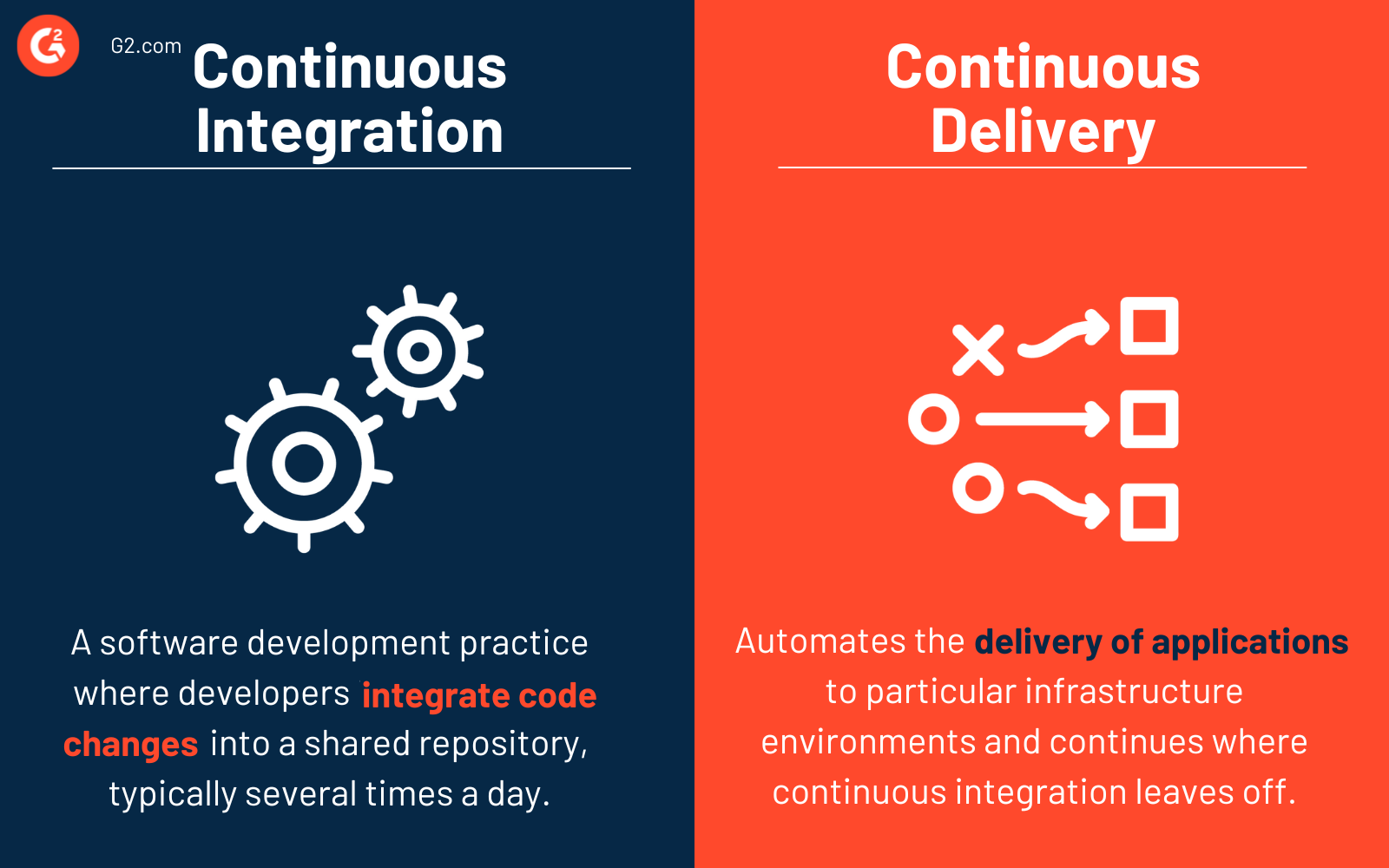
Continuous integration is a software development practice in which developers integrate their code changes into a shared repository, typically several times a day. Each integration is verified by automated build processes and tests that help to address any issues early in the development cycle.
CI aims to improve the quality of software development by catching errors and bugs as early in the process as usual and to make the development protocol more efficient by automating repetitive tasks. By continuously integrating code changes into the main codebase, developers can ensure that the code is always in a buildable and testable state and that all changes are documented.
Continuous delivery (CD) automates the delivery of applications to particular infrastructure environments and continues where continuous integration leaves off. Updates, bug fixes, and even new features verified as part of the code base are delivered to users quickly and safely through CD. It ensures that pushing code changes to various environments is automated.
Learn more about how to prevent technical debts in the software development lifecycle.

Sagar Joshi
Sagar Joshi is a former content marketing specialist at G2 in India. He is an engineer with a keen interest in data analytics and cybersecurity. He writes about topics related to them. You can find him reading books, learning a new language, or playing pool in his free time.