What is IoT security?
Internet of Things (IoT) security protects connected devices and networks against unauthorized access. It involves techniques and systems that organizations rely on to defend against cybercrime.
The IoT connects devices wirelessly. Its security is pivotal to a company’s overall cybersecurity. There have been instances in which infiltrating a typical IoT device leads to an attack on a more extensive network. IoT security is critical to ensuring the safety of devices connected across networks.
IoT security uses various techniques, strategies, and actions to safeguard vulnerabilities. Many organizations turn to IoT security software to gain better control and visibility over their IoT infrastructure and protect it against cyber attacks.
Importance of IoT security
As connected devices increase, so do the threat factors that can affect them. Here’s why IoT security is important and why enterprises should care about it.
- Remote exposure. IoT devices are easily attacked due to their exposure to internet-based activities. This means hackers can remotely connect and interact with the devices.
- Lack of industry foresight. Most industries are digitally transforming. Some, such as healthcare and automotive, have recently started expanding their section of IoT devices to be more cost-effective and productive. With a higher dependence on technology than ever before, businesses must foresee all the requirements to secure their devices. A lack of planning can expose organizations to security threats.
- Resource constraints. Some IoT devices need more computing power to integrate sophisticated firewalls or antivirus software.
How to protect IoT systems
Every industry demands safe and secure IoT devices, whether it is new to digital transformations or has already successfully implemented them. Below are some of the measures companies can take to improve data protection policies:
- Implementation of IoT security in the initial phase. Most IoT security issues discussed can be prevented by better preparation. Special care must be taken during the research and development stage itself. Enforce security by default, use the most current operating systems, and secure hardware. Be mindful of the various vulnerabilities management throughout each stage of development.
- Digital certificate. Public key infrastructure (PKI) is an excellent method to secure client-server connections between interconnected devices. PKI uses a two-key asymmetric encryption for encrypting and decrypting private messages with digital certificates. It helps protect the confidential information users enter in clear text on websites. For example, e-commerce makes use of PKI for secure transactions.
- Network security. Internet networks let potential hackers infiltrate IoT systems remotely. Networks comprise digital and physical components, and IoT security must address both access points. Examples of safeguarding the two access points include ensuring port security, using anti-malware and firewalls, and blocking unauthorized IPs.
- API security. Application programming interface (API) is the backbone of almost all sophisticated websites. For instance, travel agencies can gather flight information from various airlines in one location. However, this is also a potential area of compromise as threat factors can hack these communication channels. Therefore, it’s necessary to focus on API security to protect data sent from IoT devices to backend systems. Only authorized people, devices, and applications should interact with APIs.
- Network access control (NAC): NAC provides a baseline for tracking and monitoring IoT devices connected to a network.
- Segmentation. Devices directly connected to the internet should be segmented into different networks and given restricted access to the enterprise network. These segmented networks continuously look for suspicious activities and immediately act if any issue occurs.
- Secure gateways. They act as a throughway between networks and IoT devices. Secure gateways possess more processing power, memory, and capabilities, allowing them to implement features like firewalls so hackers can’t easily access connected IoT devices.
- Training. Security staff should stay up to date on IoT and operating system security, new or unknown systems, new architecture and programming languages, and any security threats.
IoT security best practices
It’s essential to have a proper security system for connected devices, just as there would be for traditional endpoints. Everyone should follow these best practices for strong IoT security. Below are some best practices broken down from two standpoints.
For consumers:
- Stay up to date. Get current on all patching and operating system updates the connected device needs.
- Use strong passwords. Avoid any security threats by following good password practices for all devices.
- Leverage multi-factor authentication (MFA). This practice requires users to give more than two verification factors to access a resource.
- Collect inventory. Regularly collect an inventory of connected devices and disconnect any device not in use.
For businesses:
- Implement device policy. Develop a device policy to outline how employees should register and use IoT devices. It should also describe how management will monitor, inspect, and control the devices to secure them.
- Compile all the IoT devices. The organization should have a complete list of all the IoT devices. Monitoring all the devices helps organizations understand the possible security measures needed.
- Adopt cloud-based applications. Use cloud-based applications like a cloud access security broker (CASB) as a security checkpoint between the cloud network and cloud-based applications. It helps manage possible data threats and facilitates authentication and authorization.
- Monitor devices. Take immediate action if a device shows any signs of a data threat or leak.
- Encrypt data. All data transmitted between connected devices should be immediately encrypted from its original format to an alternate one.
IoT security vs. cybersecurity
It's easy to confuse IoT security with cybersecurity, but the differences are distinct.
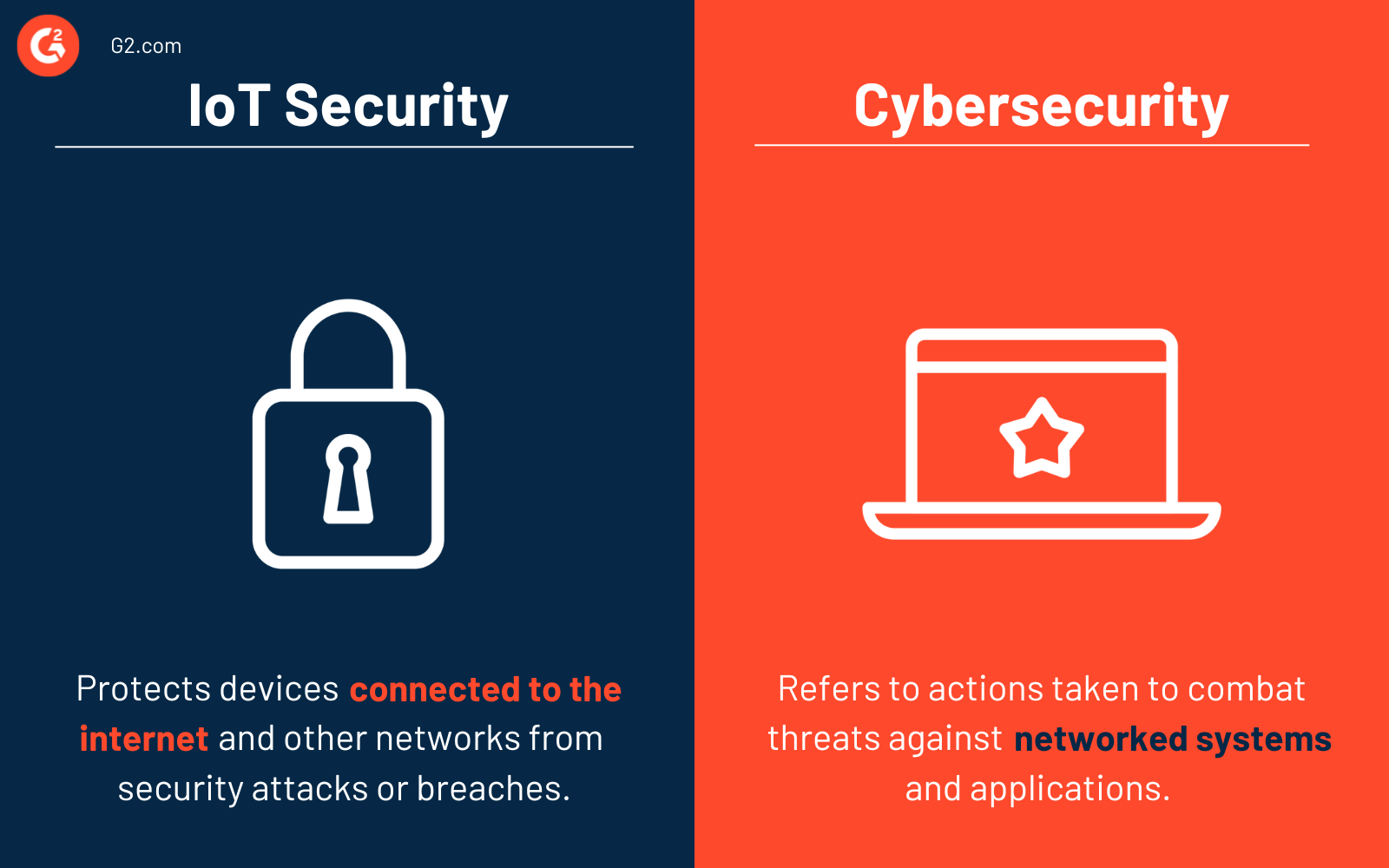
IoT security protects devices connected to the internet and other interconnected networks from security attacks or breaches. They identify, monitor, and protect IoT devices from risks and fix any vulnerabilities that threaten any organization.
Cybersecurity provides security to information systems and devices. Cybersecurity has several subdivisions, like network security, application security, or disaster recovery. IoT security is often a part of an organization’s overall cybersecurity program.
Learn more about cybersecurity to protect businesses against evolving cybercrime.

Sagar Joshi
Sagar Joshi is a former content marketing specialist at G2 in India. He is an engineer with a keen interest in data analytics and cybersecurity. He writes about topics related to them. You can find him reading books, learning a new language, or playing pool in his free time.